Documentation/ctkWorkflowWidget: Difference between revisions
From Commontk
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master/Libs/Widgets/ctkWorkflowWidget.h ctkWorkflowWidget]: a workflow with a user interface | ** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master/Libs/Widgets/ctkWorkflowWidget.h ctkWorkflowWidget]: a workflow with a user interface | ||
** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master/Libs/Widgets/ctkWorkflowStackedWidget.h ctkWorkflowStackedWidget]: a workflow with a user interface with many pages, based on a QStackedWidget | ** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master/Libs/Widgets/ctkWorkflowStackedWidget.h ctkWorkflowStackedWidget]: a workflow with a user interface with many pages, based on a QStackedWidget | ||
** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master | ** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master/Libs/Widgets/ctkWorkflowTabWidget.h ctkWorkflowTabWidget]: a workflow with a user interface with many pages, based on a QTabWidget | ||
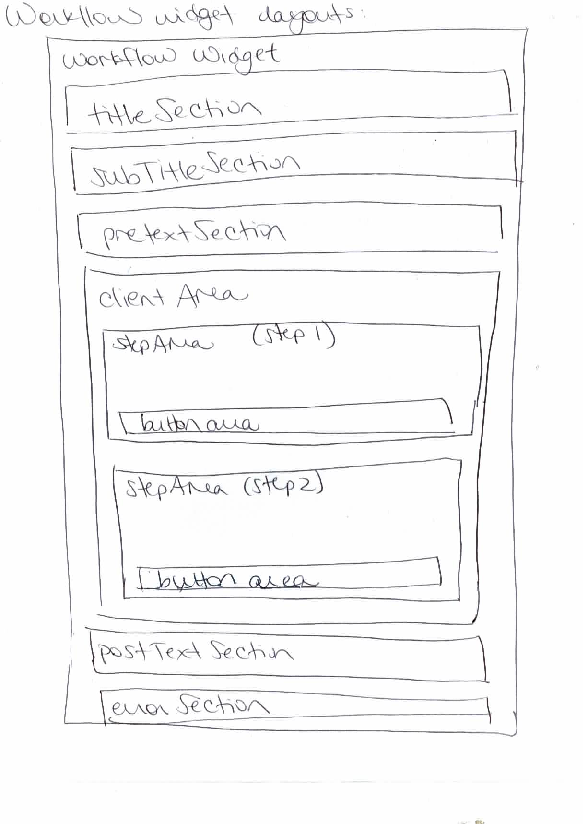
** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master | ** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master/Libs/Widgets/ctkWorkflowGroupBox.h ctkWorkflowGroupBox]: organizes display of the user interface for a particular step, including a subtitle, pre-text, client area, post-text and error text | ||
** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master | ** [https://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master/Libs/Widgets/ctkWorkflowButtonBoxWidget.h ctkWorkflowButtonBoxWidget]: a widget containing "next", "back" and "jump step" buttons | ||
== To define a new workflow step with a user interface == | == To define a new workflow step with a user interface == | ||
Latest revision as of 12:46, 13 January 2011
Home < Documentation < ctkWorkflowWidgetSummary
- Image analysis and image guided therapy procedures often have fairly complicated workflows
- CTK's workflow manager and workflow widgets provide a mechanism to construct workflows, display the appropriate user interface for each step, validatee user input and transition appropriately between steps of the workflow
- They use Qt's state machine implementation, with an additional CTK workflow manager layer
Workflow classes
- Core workflow functionality (no widgets):
- ctkWorkflowStep: a step in the workflow
- ctkWorkflow: the workflow
- ctkWorkflowTransition: a transition in the workflow
- Workflows associated with widgets:
- ctkWorkflowWidgetStep: a step in the workflow with a user interface
- ctkWorkflowWidget: a workflow with a user interface
- ctkWorkflowStackedWidget: a workflow with a user interface with many pages, based on a QStackedWidget
- ctkWorkflowTabWidget: a workflow with a user interface with many pages, based on a QTabWidget
- ctkWorkflowGroupBox: organizes display of the user interface for a particular step, including a subtitle, pre-text, client area, post-text and error text
- ctkWorkflowButtonBoxWidget: a widget containing "next", "back" and "jump step" buttons
To define a new workflow step with a user interface
- Method 1: derive ctkWorkflowWidgetStep:
- Implement validate(): evaluates user input and returns true if valid, false if not. Emits validateComplete(int) when finished.
- Implement entryProcessing(): processing that is done when entering the step. Emits entryProcessingComplete() when finished.
- Implement exitProcessing(): processing that is done when exiting the step. Emits exitProcessingComplete() when finished.
- Either:
- Implement populateStepWidgetsList(QList<QWidget*>& stepWidgetsList): add the step's widgets to the given list; by default they will be displayed vertically in the order in which they were added. Emits populateStepWidgetsListComplete() when finished.
- Implement showUserInterface() and hideUserInterface(): for more control over the step's UI. Emits showUserInterfaceComplete() and hideUserInterfaceComplete(), respectively, when finished.
- Method 2: use signals and slots
- Create an object that derives QObject
- Implement slots that mimic the functionality of validate() / entryProcessing() / exitProcessing() / populateStepWidgetsList() / showUserInterface() / hideUserInterface(), and which emit a signal when completed
- Use regular ctkWorkflowWidgetSteps in the workflow, and set their hasXXXCommands (ex. hasValidateCommand) to 1
- Connect your object's signals/slots to those of the steps/workflow
- When the workflow runs, it will emit the relevant signals to trigger your QObject's slots, which will then send indicate completion by the signals they send.
Examples
- Examples of how to create a custom workflow step:
- Method 1: ctkExampleDerivedWorkflowWidgetStep.h and ctkExampleDerivedWorkflowWidgetStep.cpp: custom step created by deriving ctkWorkflowWidgetStep
- Method 2: ctkExampleWorkflowWidgetStepUsingSignalsAndSlots.h and [hhttps://github.com/commontk/CTK/tree/master/Libs/Widgets/Testing/Cpp/ctkExampleWorkflowWidgetStepUsingSignalsAndSlots.cpp ctkExampleWorkflowWidgetStepUsingSignalsAndSlots.cpp]: custom step created by implementing the step's functionality in a class derived from QObject, and communicating with the workflow using its signal-slot mechanism
- Examples of how to create a workflow:
- Method 1: ctkExampleUseOfWorkflowWidgetUsingDerivedSteps: builds a simple workflow using custom steps that derive ctkWorkflowWidgetStep
- Method 2: ctkExampleUseOfWorkflowWidgetUsingSignalsAndSlots: builds a simple workflow using custom steps that communicate with the workflow using its signal-slot mechanism
- Examples of the workflow manager in Slicer 4:
- EM Segmenter module
Overview of state diagram underlying ctkWorkflow
- Processing step = handles user interaction, and supports additional processing (ex. image processing) as well
- Validation step = evaluates the success of the processing step
- Currently supported transitions:
- Transition to the next step
- Transition to the previous step
- Transition to a "finish" step
- Equivalent to doing "next, next, next, next..." until you hit the finish step: completes all entry/exit processing associated with each step encountered on the way to the finish step, without showing user interface.
- Success relies on the suitability of the default processing, parameters, etc
- "Blocking" steps, ex. those requiring user interaction, will prohibit success in transitioning to the finish step
- On success: transitions back to the step where the attempt to go to the finish step was initiated, so that the user can perform additional customization from there if needed.
- On failure: remains in the step whose validate() returned failure, and shows its user interface.
GUI implementation in ctkWorkflowWidget
- workflowWidget->addWidget(QWidget* widget): adds a widget to the clientArea
- workflowWidget->showWidget(QWidget* widget): shows the clientArea (i.e. for ctkWorkflowStackedWidget and ctkWorkflowTabWidget, ensures that the correct "page" is shownl
Examples
ctkworkflow w;
ctkWorkflowStep s1("select_image");
ctkWorkflowStep s2("input_new_size");
ctkWorkflowStep s3("display_resized_image");
w.addTransition(&s1, &s2);
w.addTransition(&s2, &s3);
Workflow layout
Branching workflows
s3----s4 "simple"
/
s0----s1----s2
\
s5----s6 "advanced"
Associated code:
ctkWorkflow w; ctkWorkflowStep s0; ... ctkWorkflowStep s6; w.setInitialStep(s0); [Ideally - should be optional] w.addTransition(s0, s1); w.addTransition(s1, s2); w.addTransition(s2, s3, ctkWorkflow::BiDirectionnal, "simple"); w.addTransition(s3, s4); w.addTransition(s2, s5, ctkWorkflow::BiDirectionnal, "advanced"); w.addTransition(s5, s6);
Conditional branching:
[signal] void validationComplete(bool isValid, const QString& branchId)
- ctkWorkflow::validate() doesn't give branchId:
- Single transition:
- transition created without branchId: post transition
- transition created with branchId: post transition
- Single transition:
- Multiple transitions:
- (incorrect usage) transitions created with branchIds: use first transition that was added
- Multiple transitions:
- ctkWorkflow::validate() gives branchId:
- Single transition:
- transition created without branchId: post transition (workflow overrides step)
- transition created with branchId: conditional transition based on match, if no match then stay in current step
- Multiple transitions:
- transitions created with branchIds: conditional transition based on match, if no match then stay in current step
- Single transition: